“Begin challeging your own assumptions. Your assumptions are your windows on the world. Scrub them off every once in a while, or the light won’t come in.”
1. 小米笔试
1.打印二叉树
题目描述:
在某个存储介质以如下形式保存一棵二叉树 1(2(3,4(,5)),6(7,)) 上述序列表示的二叉树如下所示:
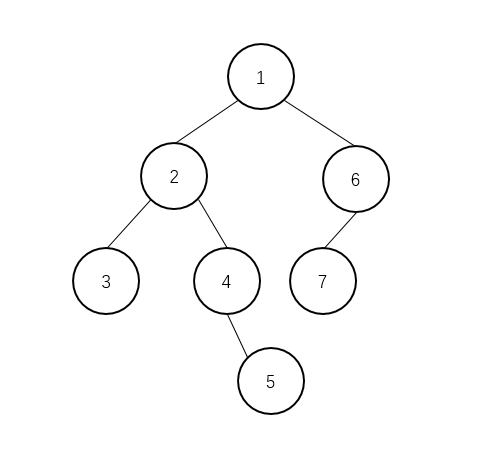
观察后可以发现,每个节点的格式为X, X可以为空或者X(Y,Z),其中X不为空。请编写程序将以上述格式输入的二叉树输出为中序遍历顺序。
输入:
上述格式表示的二叉树字符串,用字符1~9表示每个二叉树的每个节点,字符可以重复使用。
输出:
二叉树的中序遍历结果。
样例输入:
1(2(3,4(,5)),6(7,))
样例输出
3245176
解法1: 利用字符串,构建二叉树,再中序遍历得到结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
static class Node{
int val;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int val){
this.val = val;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
static void solution(String input) {
//构建二叉树
Node root = buildTree(input);
//中序遍历
infixOrder(root);
}
//非递归实现中序遍历
static void infixOrder(Node root){
ArrayDeque<Node> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
Node current = root;
while (current != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
if(current != null){
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}else{
current = stack.pop();
System.out.print(current.val);
current = current.right;
}
}
}
//Example: 1(2(3,4(,5)),6(7,))
static Node buildTree(String input){
if(input == null || input.length() == 0){
return null;
}
int i = Integer.valueOf(input.substring(0,1));
Node root = new Node(i);
if(input.length() > 1){
String child = input.substring(2,input.length() - 1);
int left = 0, right = 0, mid = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < child.length(); j++){
if(child.charAt(j) == '('){
left++;
continue;
}
if(child.charAt(j) == ')'){
right++;
continue;
}
if(child.charAt(j) == ',' && left == right){
mid = j;
break;
}
}
String leftChild = child.substring(0,mid);
String rightChild = child.substring(mid+1);
root.left = buildTree(leftChild);
root.right = buildTree(rightChild);
}
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String res;
String _input;
try {
_input = in.nextLine();
} catch (Exception e) {
_input = null;
}
solution(_input);
}
解法2: 直接遍历字符串加递归输出结果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
public static String test2Pro(String str){
String temp = "";
if(str == null || str.length() == 0){
return temp;
}
temp = str.substring(0,1); //根 1
if(str.length() > 1) {
String rest = str.substring(2,str.length()-1); // 2(3,4(,5)),6(7,)
int i = 0;
int count = 0;
while (i < rest.length()){
char t = rest.charAt(i);
if(t == '('){
count++;
}else if(t == ')'){
count--;
}else if(t == ','){
if(count == 0){
break;
}
}
i++;
}
if (i == 0){
//左子树为空
temp += test2Pro(rest.substring(i+1,rest.length()));
}else if(i == temp.length() - 1){
//右子树为空
temp = test2Pro(rest.substring(0,i)) + temp;
}else{
//左右子树都不为空的情况
temp += test2Pro(rest.substring(i+1,rest.length()));
temp = test2Pro(rest.substring(0,i)) + temp;
}
}
return temp;
}
2.打印二叉树
题目描述
小米之家有很多米粉喜欢的产品,产品种类很多,价格也不同。比如某签字笔1元,某充电宝79元等等。假设库存不限,小明去小米之家买东西,要用光N元预算的钱,请问他最少能买几件产品?
输入:
1
2
3
第1行为产品种类数
接下来的每行为每种产品的价格
最后一行为预算金额
输出:
能买到的最少的产品的件数,无法没有匹配的返回-1
样例输入
1
2
3
4
2
500
1
1000
样例输出
1
2
解法1:(此题是leetcode 322 零钱兑换的原题。为此,参考leetcode上面Labuladong的题解,给出本文相关的解法)首先是暴力递归法求解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
//暴力递归法
public static int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount){
if(amount == 0){
return 0;
}
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int coin : coins){
if(amount < coin){
continue;
}
int subProb = coinChange(coins, amount - coin);
if (subProb == -1){
//子问题无解
continue;
}
ans = Math.min(ans,subProb+1);
}
return ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : ans;
}
解法2:带备忘录的递归算法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public static int coinChange1(int[] coins, int amount){
int[] memo = new int[amount+1];
//备忘录初始化为-2
for (int i = 0; i < amount+1; i++){
memo[i] = -2;
}
return helper(coins,amount,memo);
}
private static int helper(int[] coins, int amount, int[] memo){
if (amount == 0){
return 0;
}
if(memo[amount] != -2){
return memo[amount];
}
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int coin : coins){
if(amount - coin < 0){
continue;
}
int subProb = helper(coins,amount-coin,memo);
if (subProb == -1){
continue;
}
ans = Math.min(ans,subProb+1);
}
memo[amount] = (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? -1 : ans;
return memo[amount];
}
解法3:动态规划求解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt();
int[] ps = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ps[i] = in.nextInt();
}
int m = in.nextInt();
System.out.println(solution(ps,m));
}
public static int solution(int[] coins, int amount){
int[] dp = new int[amount+1];
//初始化dp数组
for (int i = 1; i < dp.length; i++) {
dp[i] = amount+1;
}
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1;i <= amount; i++){
for (int coin: coins){
if(coin <= i){
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i],dp[i - coin] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
}